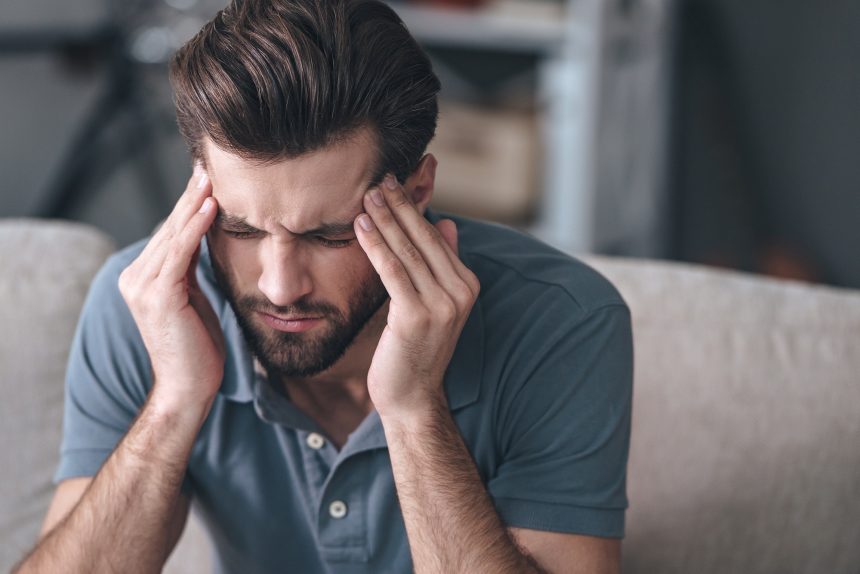
According to the WHO, between 50% and 75% of adults worldwide have had a headache in the past year. For some people, headaches may be more severe or more frequent.
Your headache location and type can give you clues about what’s causing your headaches and how to solve the problem. If you pay attention to your headache location and meaning, you can reveal some things about your health.
Let’s take a look at the most common headache locations and types of pain.
Most Common Headache Location and Meaning
Headache location types can help you determine what kind of headache you may have. Occasionally there are other causes for a certain headache location too.
Pain at the back of your head or neck is often a tension headache or migraine. It could be arthritis or occipital neuralgia. Top of your head pain is usually a tension headache but could be migraine, occipital neuralgia, hypertension, or aneurysm.
If you have pain in your forehead, cheeks, or behind both eyes, it is probably a tension headache or migraine. It could be a cluster headache or sinus infection.
A cluster headache might show up as pain behind one eye, though the same pain may indicate migraine, occipital neuralgia, eye infection, or aneurysm. Pain in the temples could indicate a tension headache, cluster headache, migraine, TMJ, or temporal arteritis.
If you have pain behind the ear, it’s most likely an ear infection. Alternatively, it could be a sinus infection, dental problems, occipital neuralgia, TMJ, or mastoiditis.
If you have pain on one side of your head it is usually a cluster headache or migraine. Rarely, it could be an aneurysm or hemicrania continua. If your head hurts everywhere, it’s probably a tension headache. However, it could be a migraine or sinus infection.
Consider Headache Types of Pain
The type of pain you are experiencing can also give you some clues to your health. Pay attention to the pain and any other symptoms.
Headaches that are a dull, tightening feeling but don’t throb are usually tension headaches. Your head may also be tender to the touch. Tension headaches are very common and can be caused by a number of things including stress, lack of sleep, eyestrain, or allergies.
If your pain is throbbing and lasts for some time or comes with changes to your vision or nausea, you may be experiencing a migraine. For many, light and noise make the pain worse.
Cluster headaches usually come on quickly but don’t last long. They are usually a sharp, searing, one-sided pain that may happen repeatedly for several days.
If you have pressure or tenderness in your face along with cold-like symptoms, you might have a sinus headache.
When to Seek Help
Over-the-counter pain relievers may help with tension headaches and migraines. If you have severe or repeated migraines or cluster headaches, you may want to talk to your doctor about other treatment possibilities.
Electrocardiography and ultrasound therapy may help if your headaches are caused by heart or other cardiovascular issues. You can view more here to learn more about this type of therapy.
If you are worried about possibly more serious conditions, you should seek treatment from your physician.
Pay Attention to Your Types of Headache Areas
If you have a headache, think about where it hurts and what kind of pain it is. Doing so can help you figure out how headache location and meaning are related and can give you clues about your health.
If you found this article helpful, be sure to read our other health articles too.