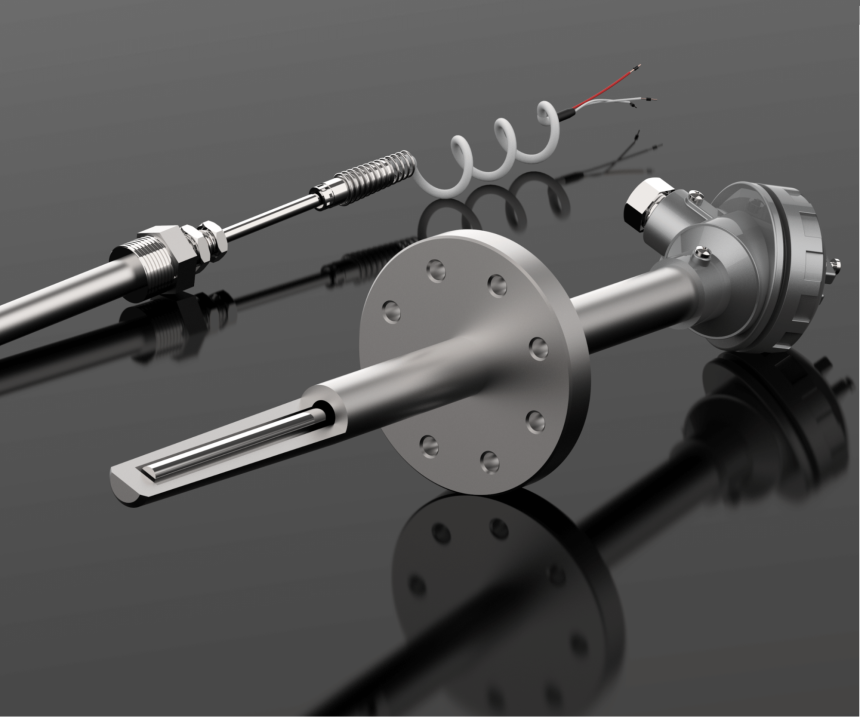
For accurate temperature monitoring and management, a well-designed sensor is a foundation. Temperatures between (−) 200°C and 500°C and up to 800°Con are measured with a resistance temperature detector. The resistive element must be compatible with instrumentation and a physical structure that allows for the best thermal response to the process fluid measuring. A sensor whose resistance changes as its temperature changes are called as mineral-insulated RTD. As the sensor’s temperature rises, the resistance increases as well. An RTD is a passive gadget that doesn’t generate an output itself. A small electrical current is run through the sensor to produce a voltage, which is then utilised to measure the sensor’s resistance by external electronic devices.
Let’s see about the mineral-insulated RTD sensors and the working principle of an RTD sensor:
What is Mineral insulated?
Mineral-insulated cable was created with important circuit protection in mind and is perfect for protection in constructions like high-rises, subways, tunnels, airports, healthcare institutions, industrial, and petrochemical plants. Only inorganic elements, such as copper and magnesium oxide, are used in constructing mineral insulated RTD sensors, which provides an exceptional balance of dependability and performance.
What is an RTD Sensor?
An RTD is a passive temperature-sensing device that works because temperature changes cause a change in a metal’s resistance. According to the resistance properties of the RTD sensor, the resistance value produced by the electrical current flowing through the element or resistor of the sensor is measured by a connected instrument and related to the temperature.
How does an RTD sensor work?
An RTD sensor operates on a reasonably simple basis. When a metal’s temperature rises, it becomes more resistive in all its forms. Temperature readings can be obtained by measuring the resistance. Due to their accuracy and tolerance to extreme temperatures, vibrations, and shock, RTD sensors have become a crucial component of manufacturing and sensitive temperature processes. The sensor is turned on using a little amount of DC current to prevent overheating from excessive current.
Before installing the Mineral Insulated RTD sensor, it is advised to attach a thermowell, and a closed-end tube. Heat is transferred from the process to the thermowell wall and then to the sensor. In order to place sensing equipment without creating a hole in the line, a thermowell is a thermally conductive extension that is fitted into a process line.
What are Mineral Insulated RTD sensors?
Compacted magnesium oxide is used to create Mineral Insulated RTD sensors, which are sturdy and vibration-resistant. The chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries frequently employ this line of goods. Since it complies with IEC 751, the measuring element of Mineral Insulated RTDs can be built in various ways. The sensors’ weatherproof aluminium heads shield the interior structure from the elements. The mineral insulated sheaths can be quite lengthy and bent or coiled depending on the application.Mineral insulated RTDs with terminal heads are quite useful since the mineral insulated sheaths can be made very long and twisted or coiled depending on the application.
RTD sensors types
There are two different types of resistance temperature detector. Their design is determined by how the temperature-sensing device is built. Thin-film elements are found in the second category, whereas wire-wound elements are found in the first.
Thin-film RTDs
A thin coating of metal, typically platinum, is deposited on a ceramic substrate material to create the thin-film RTD components. An electrical circuit pattern is laser cut or etched into the metal layer to achieve the required resistance level. The entire element is covered with a thin protective glass layer before adding lead wires.
The reliability and inexpensive cost of production of thin-film RTDs are its advantages. Moreover, compared to other resistance temperature detectors, they are more vibration damage resistant.
Wire-wound RTDs
The alternative RTD type is wire-would. A tiny coil of fragile platinum wire makes up its sensing component. The wire coil can also be wrapped around the outside of the housing material, however it is often housed inside a ceramic or glass tube.
The benefits of wire-wound RTDs include their great accuracy, the ease with which those with glass cores can be submerged in various liquids, and the ability to measure extremely high temperatures with those with ceramic cores precisely.
Wrapping it up
Hopefully, you will learn about mineral insulated RTD sensors and the working principle of an RTD sensor. A sensor used to measure temperature is called an RTD. An electrical current is used to pass through the resistance element, which measures the resistance of the current being carried through it, to the sensor.Electrical resistance increases along with a resistance element’s temperature rise.
Also read: Early fire detection in coal yard bunker