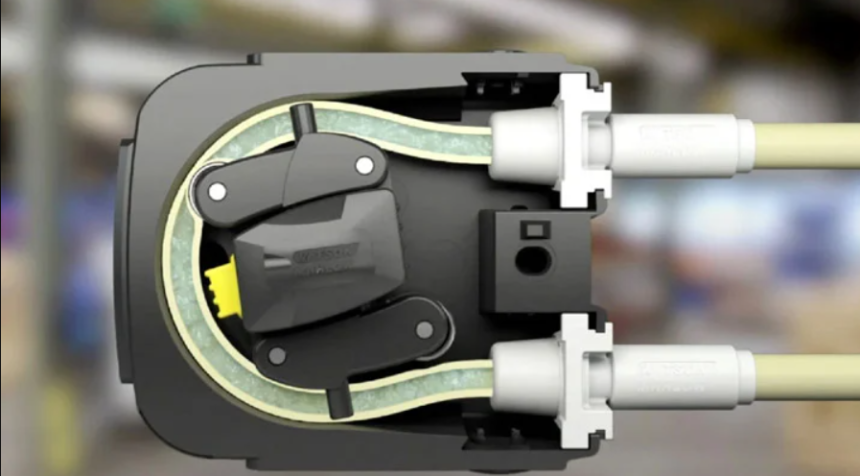
The equipment chosen in laboratories can significantly alter test results. Among the different types of equipment, peristaltic pumps stand out for their flexibility and accuracy. Their unique mechanism enables versatility, making these pumps integral to many, if not most, lab applications.
Peristaltic Pump Basics
Peristaltic pumps have a simple yet effective mechanism of action. Fluid is drawn through a flexible tube or hose, where the inflating action of rotating rollers creates a partial vacuum. This process simulates natural peristalsis, the method used to move substances through organs in biological systems. The accuracy of this design makes peristaltic pumps ideal for lab operations where precision is essential.
Advantages of Peristaltic Pumps
Precision and Control
Peristaltic pumps are renowned for their high level of accuracy, which is one of their many advantages. These pumps provide precise measurements and are often used in laboratories for this reason. Flow rates can be accurately controlled by adjusting the rollers’ speed and the tubing’s diameter. This level of control is crucial for experiments that require uniform and replicable conditions.
Reduced Contamination
Contamination is a significant concern in any laboratory. Peristaltic pumps help mitigate this risk by ensuring that fluids are only in contact with the inner tubing. The use of sterile and disposable tubing ensures that no sample cross-contamination occurs. This is particularly advantageous in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications, where sterility is critical.
Versatility
From viscous fluids to delicate cell cultures, peristaltic pumps can handle a wide variety of fluids. They are capable of operating with different fluid properties, making them useful for many applications. For instance, they can pump corrosive chemicals or materials that are sensitive to shear, all while maintaining the integrity of the sample.
Ease of Use
Peristaltic pumps feature a simple design, making them easy to operate. With fewer moving parts than other types of pumps, they require minimal maintenance. Most issues can be resolved by replacing the tubing, which minimizes downtime and ensures the lab remains operational.
Durability and Longevity
Built to withstand the demanding conditions of a laboratory, peristaltic pumps are constructed from high-quality materials that last for long periods. This durability means less frequent replacements and repairs, leading to reduced costs and increased reliability.
Various Applications in Laboratories
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Peristaltic pumps play a vital role in biotechnology processes such as fermentation and cell culture. Their gentle handling of fragile biological materials is a significant advantage. Additionally, pharmaceutical laboratories use peristaltic pumps to control dosing accuracy, which is essential in drug formulation and testing.
Chemical Processing
Peristaltic pumps are ideal for the controlled delivery of aggressive chemicals. The selection of tubing materials that are compatible with specific chemicals ensures safe operation. This flexibility is particularly valuable in research and development environments, where multiple chemicals may need to be handled with care.
Environmental Testing
In environmental laboratories, peristaltic pumps are used to analyze soil and water. These pumps help transfer liquids accurately, which is crucial for reliable test results. Designed for portability, they can also be used in the field, offering versatility for environmental assessments outside the lab.
Economic and Environmental Factors
Cost-Effectiveness
While peristaltic pumps may require a higher initial investment, their long-term benefits far outweigh the initial costs. With less maintenance, reduced downtime, and a longer lifespan, these pumps result in significant savings over time. This makes them a cost-effective option for labs, enabling more efficient resource allocation and improved productivity and research quality.
Eco-Friendly Operation
Peristaltic pumps also support sustainability and waste reduction. The disposable tubing requires minimal cleaning and conserving water and chemicals. Moreover, their precise operation minimizes waste, contributing to environmentally conscious lab practices.
Conclusion
Peristaltic pumps have become indispensable laboratory tools, offering precise, flexible, and reliable performance. Their distinct benefits—from contamination reduction to the ability to handle diverse fluids—make them suitable for various applications. By investing in peristaltic pumps, labs can save time, enhance safety, and contribute to sustainability. As technology evolves, these pumps are expected to play an even larger role in scientific research, supporting progress in areas from environmental monitoring to astronomy.