Origin of Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts traces its origin to 1994 when Nick Szabo came up with an innovative idea of recording contracts in form of computer code. Szabo toiled hard for many years over this idea while burning the midnight oil to write a book named “Smart Contracts: Building blocks for Digital Free Markets” but the main issue was that Blockchain was non-existent at that time.
Later in 2009 Blockchain technology was introduced by Bitcoin, but finally, in 2015, Vitalik Buterin made use of Smart Contracts in Ethereum.
What is a Smart Contract?
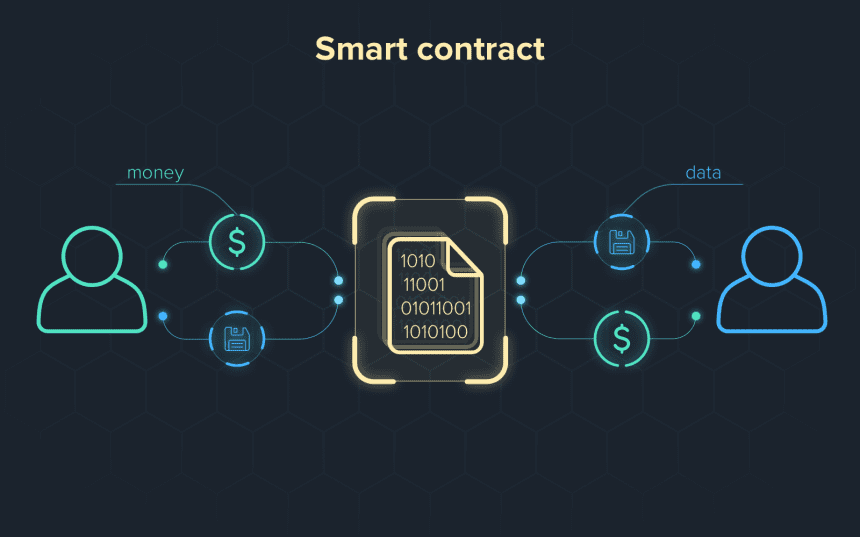
A Smart contract is an agreement, which is a contract that self-executes when certain mentioned conditions are met. Such sort of contract is written into lines of computer code to facilitate easy transactions between buyer and seller. The fair and trustless nature of smart contracts eliminates the need for a third party to do verification and this results in saving time. These codes and agreements of smart contracts would spread across the nodes of distributed and decentralized Blockchain networks. This means that the transactions are trackable but immutable, as it’s near impossible to alter all nodes.
The above makes it clear that a Smart Contract is neither really ‘smart’ nor contracts bind a person in a legal sense. A Smart Contract is more like a business rule fed into the software and to be simple they are code that does what it’s been programmed to do.
How does Smart Contracts work?
Before a Smart Contract Development is done, the contractual parties must determine the terms of the contract. When the contractual terms are finalized, they are written into a programming code where their terms are translated into the computer language. This code contains a number of different conditional statements that describe the possible scenarios of a future transaction.
The created code gets stored in the Blockchain network, where it is replicated among the participating nodes in the network. Whenever this code is run and if the term of the contract is satisfied, then all the nodes in the network verify it so that the relevant transaction gets executed.
How Smart Contracts are created?
Smart Contracts are generally created by Smart Contract Development Companies, and they can do that over multiple Blockchain platforms. Different Blockchain platforms use different languages for writing Smart Contracts, but here let’s take example of Ethereum, which is one of the most popular and versatile platforms for deploying Smart Contracts. Solidity language is used in Ethereum for writing Smart Contracts, which is its original coding language.
Some use-cases of Smart Contracts across industries
Insurance sector
The experiment of employing Smart Contracts for insurance happened a few years back in 2017 when two insurance companies tested it. The insurance companies named Atlas and Axa worked with their prototypes to compensate airline customers if their flights were delayed. This system saves a lot of time and effort for a traveler and streamlines the claims process for the airline company, as everything here is automated.
Healthcare sector
The use of Smart Contracts in the healthcare industry can be done to record and transfer patient data safely. EncrypGen is an application that utilizes the smart contract to transfer patient data without allowing any access from third parties. This system lets researchers use the patient data for research but for that, they need to pay for it, while the data is in the control of the patient and they can only decide whether they want to sell it.
Government departments
Governments can employ smart contracts over Blockchain to ensure a fairer and trustless voting process. There are applications using smart contracts and blockchain technology to collect votes and protect them from fraud. Blockchain technology ensures that once a vote is casted cannot be changed and a smart contract will automate the process of sending a token to an address that represents the winner of the vote.
Business management
Smart Contracts would let businesses automate a lot of things in their organization like streamlining the payroll process. It would save the costs and hassle of having personnel for monitoring the attendance of the workforce.
Future of Smart Contracts
The massive growth in the IoT connected devices and automation will certainly push toward the greater use of smart contracts. The Smart contract experts at Rejolut say that when blockchain and IoT are combined they could actually transform vertical industries, as there is a heavy focus on process efficiency, supply chain, and logistics opportunities.