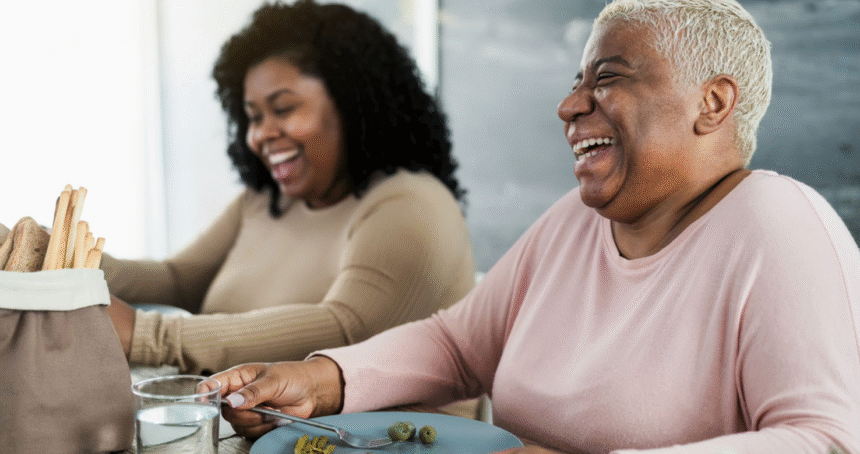
As we age, maintaining a healthy diet becomes increasingly important—but for many seniors, eating can become a challenge. Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or digesting food can lead to malnutrition, weight loss, and decreased quality of life. Understanding these challenges and learning how to manage them is essential for both seniors and their caregivers. In this post, we’ll explore common causes of eating difficulties in older adults and provide practical strategies to make mealtime easier and more enjoyable.
- Common Causes of Eating Difficulties in Seniors
- Practical Tips to Make Eating Easier
- 1. Modify Food Texture
- 2. Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
- 3. Encourage Regular Mealtimes
- 4. Create a Comfortable Eating Environment
- 5. Maintain Oral Health
- 6. Stay Hydrated
- 7. Seek Professional Guidance
- Supporting Seniors Emotionally
- In Conclusion
Common Causes of Eating Difficulties in Seniors
Several factors can contribute to eating challenges in older adults. One of the most common issues is dysphagia, a condition that makes swallowing difficult. Dysphagia can result from stroke, neurological disorders, or even natural age-related changes in muscle strength. Difficulty swallowing can make it painful or risky to eat certain foods, increasing the chance of choking or aspiration.
Dental problems also play a significant role. Missing teeth, poorly fitting dentures, or gum disease can make chewing uncomfortable, leading seniors to avoid certain foods—especially harder fruits, vegetables, or proteins—potentially creating nutritional gaps.
Other contributing factors include loss of appetite, often caused by medications, depression, or underlying medical conditions, and digestive issues such as acid reflux or slower metabolism. Even cognitive conditions like dementia can affect a senior’s ability to remember to eat or recognize hunger cues.
Practical Tips to Make Eating Easier
While these challenges may seem daunting, there are effective strategies to help seniors maintain proper nutrition and enjoy mealtimes.
1. Modify Food Texture
Softening foods or preparing them in smaller, manageable pieces can make a huge difference. Steaming vegetables, mashing potatoes, or offering tender cuts of meat can reduce chewing difficulty. For those with more severe swallowing issues, pureed meals or thickened liquids may be recommended. Always consult a healthcare professional to ensure safety.
2. Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
Even if portion sizes are smaller, the focus should be on quality nutrition. Foods rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals help maintain strength and energy. Eggs, yogurt, soft cheeses, smoothies, and fortified soups are excellent choices that are easier to chew and swallow.
3. Encourage Regular Mealtimes
Consistency can improve appetite and digestion. Offering smaller, more frequent meals rather than three large meals can help seniors consume enough calories without feeling overwhelmed. Snacks like nut butters on soft bread, fruit smoothies, or soft-cooked vegetables can provide additional nutrition throughout the day.
4. Create a Comfortable Eating Environment
The setting matters. Bright, well-lit dining areas, comfortable seating, and minimal distractions can make mealtimes more pleasant. Eating with family or friends may also increase appetite and motivation to eat.
5. Maintain Oral Health
For seniors, regular dental checkups, proper denture maintenance, and good oral hygiene are vital. Addressing dental problems early—including considering affordable dental implants in Schererville—can reduce discomfort, improve chewing, and support overall nutrition.
6. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can reduce appetite and cause fatigue. Offering water, herbal teas, and soups throughout the day ensures seniors stay hydrated, which is particularly important for digestion and overall health.
7. Seek Professional Guidance
If eating difficulties persist, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. A dietitian can design a tailored meal plan, while a speech-language pathologist can provide exercises and techniques for safe swallowing. Early intervention can prevent complications such as malnutrition or aspiration pneumonia.
Supporting Seniors Emotionally
Eating difficulties can be frustrating and sometimes socially isolating for seniors. Patience and encouragement are key. Involving seniors in meal planning or preparation, celebrating small successes, and offering reassurance can improve both nutrition and emotional well-being.
In Conclusion
Difficulty eating is a common but manageable challenge for older adults. By understanding the causes and implementing practical strategies—like modifying food textures, encouraging regular meals, maintaining oral health, and seeking professional support—caregivers can help seniors enjoy mealtimes while ensuring proper nutrition. With the right approach, eating can remain a pleasurable and nourishing part of daily life, supporting both physical health and emotional happiness.